What is docker?
5 February 2023Docker is an open-source tool created in 2013 by Solomon Hykes, which allows us to package and deploy applications securely and efficiently. With Docker, we can ensure that our applications will work consistently in any environment.
Docker is a technology that is gaining more and more ground in the tech industry. With its ability to create and manage application containers, this tool offers an efficient and flexible solution for deploying and executing applications. Due to its growing importance, it is essential to have at least a basic knowledge of Docker’s key concepts.
It is therefore essential to have a basic understanding of the following Docker concepts:
In this article, we will explain each of these concepts, as well as how Docker achieves efficiency and security when executing our applications.
But before we do that, let’s make a small introduction about how we can use Docker on our machine.
How to use Docker?
In order to use Docker, we must install the Docker Desktop tool on our system, which we can find on the Docker official website
It is important to know that in order to use Docker on Windows, we will need to install WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux), so we will need to go to the official installation guide for WSL and install it.
What is Docker Desktop?
Docker Desktop is a platform that has the necessary tools to run our containers.
Among these tools, we have:
- Docker Engine: it is the Docker engine that allows containers to be executed and provides a command-line interface to interact with it.
- Docker CLI: it is a Docker command-line interface to interact with the Docker Engine and perform tasks such as running containers, creating images, managing networks, etc.
- Docker Compose: it is a tool that allows us to define and run multi-container composite applications.
- Docker Machine: it is a tool that allows us to create and manage virtual machines that run Docker Engine.
How does Docker achieve efficiency?
Docker uses a container system to run our applications efficiently and securely, which allows for greater portability and efficiency in the development and management of applications.
This portability ensures that our application will run on any machine and solves potential future problems by bringing our application from one machine to another.
In addition, by using containers instead of full virtual machines, performance is greatly improved and it is lighter than a virtual machine.
What is a container?
Containers are isolated environments which have all the necessary configurations and dependencies to run our images efficiently.
You could think that these are virtual machines since they work in a similar way to these, for that reason it is important to know that these NOT are virtual machines and to know the reason why the containers and the virtual machines have similar concepts but they are not the same.
Why are containers not virtual machines?
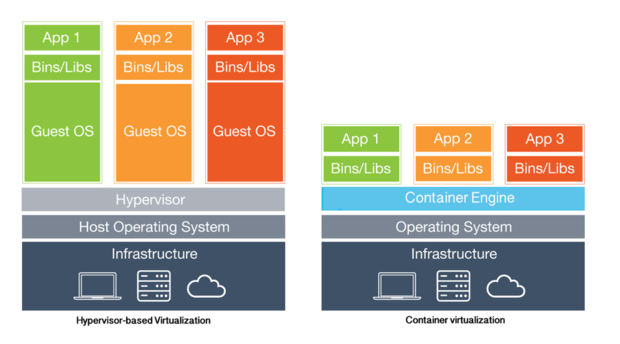
Let’s see an image to better explain how a virtual machine and a container works within our system.
This diagram has been obtained from the page infoworld.com and the authorship of this one belongs to this page.
On the left is how a virtual machine works and on the right is how a container works.
Within this diagram you can see differences between the virtual machine and the container, one of them is that all containers run within the Docker Engine instead of having installed a complete operating system for each system as we have with virtual machines, this helps a lot to improve the performance of our applications within Docker and optimize the disk space they occupy.
This gives us greater portability, faster startup time and more efficient use of resources, which is critical to the deployment and optimization of our application, and also helps reduce the costs associated with servers.
What is an image?
A Docker image is a file that contains all the necessary elements to run an application in a container, including source code, configuration files, libraries and necessary resources.
Once our image is created we can use it inside one or more containers running from it.
What is a volume?
A Docker volume is a way to persist data generated by a container, which unlike data stored inside the container that will be deleted once the container is removed or stopped, persists even when the container is removed.
These can be shared and reused between different containers and allow the separation of the data from the application configuration to be maintained. This allows for greater flexibility and ease of data management in Docker environments.
For example, imagine that we have a test database inside a Docker container and when we delete or restart our container we lose all the data and we have to reinsert it, this would make us lose a lot of time inserting the data again, right? Well, this would be solved using a volume, since it would save our entire database and when the container is lifted again, all the data would be available again.
What is dockerizing an application?
Dockerizing an application consists of packaging it in a Docker container to facilitate its distribution and execution in any environment. This allows for greater portability, flexibility and isolation of the application from its execution environment.
What are Docker networks?
Docker networks are a way to enable communication between containers and allow access to the internet. Docker networks can be managed by Docker Engine and can be configured to be private or public, allowing access only to specific containers or to all containers on a host.
In addition, Docker networks can be configured to use different types of connections, such as Bridge, Host, None, and Overlay. These different types of connections allow you to choose how containers communicate and connect to the network.
What is the Docker Hub?
Docker Hub is a cloud service that stores container images and allows sharing them with the community. It is a centralized repository where users can publish, download and share images.
What is Docker Compose?
Docker Compose is a container orchestration tool in Docker that allows you to define and run applications composed of multiple containers.
With Docker Compose, you can describe all the services, volumes and networks your application needs in a single file, and then create and start all the services at once, in a single command.
This simplifies the process of configuring and provisioning applications, which is especially useful in development and production environments.
Let’s see what a docker-compose.yml file would look like, in this one we are creating a Postgres database:
version: '3'
services:
db:
image: postgres:14.1-alpine
restart: always
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
ports:
- '5432:5432'
volumes:
- db:/var/lib/postgresql/data
What is the Dockerfile?
The Dockerfile is a plain text file that contains all the instructions needed to build a Docker image.
These instructions include which operating system to use, which packages or applications to install, which scripts to run, among others. The resulting image can be used to create and run containers in any Docker-compatible environment.
The Dockerfile is a key part of the application dockerization process and can be shared and reused to simplify the deployment of applications in different environments.
Let’s see what a Dockerfile file would look like in which we dockerize a backend made in Nestjs:
FROM node:18-alpine3.15
RUN mkdir -p /var/www/backend
WORKDIR /var/www/backend
COPY . ./var/www/backend
COPY package.json tsconfig.json tsconfig.build.json /var/www/backend/
RUN yarn install --prod
RUN yarn build
RUN adduser --disabled-password adminUser
RUN chown -R adminUser:adminUser /var/www/backend
USER adminUser
RUN yarn cache clean --force
EXPOSE 3000
CMD [ "yarn","start" ]
Docker use cases
Docker has several use cases, let’s highlight some of them:
Development & Testing
Application Distribution
Infrastructure automation
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Production environments
Conclusions
In conclusion, Docker is a powerful and versatile tool that allows you to package and deploy applications in an isolated and portable environment, ensuring that they work consistently in any environment.
In addition, Docker Hub allows us to share and download images easily. In short, Docker offers a flexible and efficient way to develop, distribute and run applications in any environment, making it an essential tool for any developer or system administrator.